Stardust
August 20, 2014
I don't know why
American songwriter,
Hoagy Carmichael, decided to name his classic 1927
composition, "
Stardust." Although there is such a thing as "
star dust," this is an odd juxtaposition of words for someone who isn't an
astronomer. Then again, this is a strange song, since it's a song-about-a-song. Strange though it is, it was popular enough for the
US Library of Congress to add Carmichael's 1927 recording of it to the
National Recording Registry.[1]
Stardust, or
cosmic dust, is formed by
stars, which emit the dust slowly, or in violent
supernovae. The dust, with particle size ranging up to about a hundred
micrometers, goes into building the
next generation of stars, but most of it floats between stars. In the early days of
astronomy, when all observations were in the
visible light spectrum, the dust was a nuisance, since it obscured astronomical objects.
Darkening of the
night sky by cosmic dust was once considered as the solution to
Olber's paradox, which reasoned that the night sky should be white, not black. The reasoning was that there would always be a star at every small patch of sky in a
universe of
infinite age and extent populated by an infinite number of stars.
Kepler saw this as an argument that the universe was finite; but, if there are obscuring dust
clouds, wouldn't this also explain the dark night sky?
In reality, this couldn't be the case, since the dust would eventually
heat to
incandescence as it reaches a
thermodynamic equilibrium with the the
energy emitted by the stars. What actually causes the dark night sky is cosmic
redshift. Because of the
expansion of the universe caused by the
Big Bang, the
light of older stars is shifted into the
infrared, and the earliest light of the universe has shifted all the way to
microwave frequencies as the
cosmic microwave background.
Today, most astronomical observations are done outside the visible light spectrum, and observations of the infrared emission of cosmic dust have elucidated properties of our
Milky Way Galaxy.
NASA's Stardust spacecraft was launched on February 7, 1999, to collect dust samples from the diffuse region around
comet,
Wild 2.
As I wrote in a
previous article (Carbon Nano-Aerogel, March 14, 2011), the Stardust dust collector was an
aerogel, as shown in the photograph. Since the Stardust spacecraft was also flitting around space for an extended period before the return of the comet dust samples to Earth in January, 2006, it had a secondary mission to collect cosmic dust.[2]
A recent article in
Science,
authored by 67
scientists from various international institutions, plus 30,714
Stardust@home "dusters," presents evidence that the
Stardust Interstellar Dust Collector captured seven interstellar dust grains.[3-8] Interestingly, fifty particles of spacecraft
debris were captured, also.[3] The seven particles are diverse in size,
elemental composition, and
crystal structure, and they present some essential data for
theorists.[3]
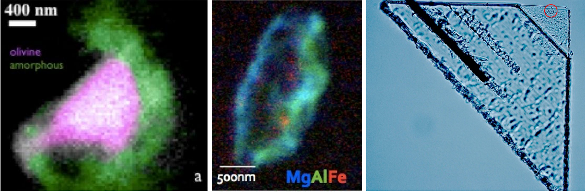 |
| Interstellar dust particles collected by NASA's Stardust spacecraft. The left image is the so-called Hylabrook dust mote, showing olivine crystals (red) surrounded by noncrystalline magnesium silicate. The center particle, called Orion, also contains the crystalline minerals, olivine and spinel, plus an amorphous material comprised of magnesium, and iron. The right image is the 35 micrometer track of a 3 picogram particle that vaporized on impact. (Left image, from STXM data, by Anna Butterworth, via UC Berkeley; center image, Westphal et al. 2014, Science/AAAS, via DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Press Release; right image, Westphal et al. 2014, Science/AAAS, via DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Press Release. |
Since cosmic dust grains travel at high speeds, up to 5
kilometers/
second, the aerogel was designed to gently slow them for capture.[8] The first hurdle in analysis was the "
needle in a haystack" problem of detecting the expected few, small grains in the large aerogel
volume. This task was
crowd-sourced to a team of more than 30,000 "dusters," who scanned millions of
Internet images of slices of the aerogel looking for particle tracks. The images were obtained by changing the
focus of a
camera to image at different depths.[5]
More than a hundred tracks were flagged in this first analysis of just 77 of the 132 aerogel panels.[4-5] Twenty-nine of these were found to have been particles ablated from the spacecraft itself. In the end, a careful analysis of impact
direction was required to identify 31 tracks for careful analysis, and three interstellar dust particles were found in the aerogel.[6-7] The Internet
volunteers did the equivalent work of a single person working forty hours a week for three years.[5]
Four additional particles were found in the
aluminum foil that surrounded the aerogel.[6] The aluminum foil was not intended as a dust collector, but scientists try to extract as much data as they can from expensive projects.[5] These particles contained the unexpected element,
sulfur.[4] Said
physicist Rhonda Stroud of the
Naval Research Laboratory,
"They were splatted a bit, but the majority of the particles were still there at the bottom of the crater... Their diversity was a surprise, but also these fluffy particles, sort of like a tossed salad, were complex, an agglomeration of other particles, rather than one dense particle suggested by the simplest models of interstellar particles."[5]
At this time, all particle analysis has been
non-destructive. Says Andrew Westphal, a physicist at the
University of California, Berkeley,
Space Sciences Laboratory and the lead author of the Science paper, "Despite all the work we've done, we have limited the analyses on purpose... These particles are so precious. We have to think very carefully about what we do with each particle."[4] The seven particles are each a different
silicate, and the two largest particles have a fluffy composition, similar to that of a
snowflake, while only
dense particles were expected.[4]
Fifty-five aerogel panels still haven't been searched for particle tracks, but the most interesting analysis would necessarily be destructive. That would be a measurement of the relative abundance of three
stable isotopes of oxygen. The abundance
ratios would confirm that the particles came from outside the
Solar System.[4] The Internet search for additional particles has just begun, and a search for tracks in the aluminum foils will be added to the Internet effort.[4]
Aside from NASA, additional funding for Stardust has come from the
Klaus Tschira Foundation, the
Tawani Foundation, the
German Science Foundation, and the
National Fund for Scientific Research,
Flanders, Belgium.[4]
References:
- You can hear Hoagy Carmichael's original version of Stardust on YouTube, here. The popular Nat King Cole cover is here, and Frank Sinatra's version is here.
- Stardust Mission Page, NASA.
- Andrew J. Westphal, et al., "Evidence for interstellar origin of seven dust particles collected by the Stardust spacecraft," Science, vol. 345, no. 6198 (August 15, 2014), pp. 786-791.
- Release Kate Greene, "Mysteries of Space Dust Revealed," Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory Press Release, August 14, 2014.
- Robert Sanders, "Seven tiny grains captured by Stardust likely visitors from interstellar space," University of California Berkeley Press Release, August 14, 2014.
- Michael D. Lemonick, "Captured Space Dust Is Probably From Beyond Our Solar System," National Geographic, August 15, 2014.
- Ian Sample, "Dust from beyond our solar system fell to Earth from space probe," The Guardian (UK), August 14, 2014.
- Maria Dasi Espuig, "Cosmic grains pre-date Solar System," BBC, August 14, 2014.