Gigayear Data Storage
November 25, 2013 If your office is similar to my office, you have stacks of digital media that are not readable on your present computer. There's the stray 3-1/2-inch floppy diskette, perhaps some 5-1/4-inch floppy disks, and a few ZIP disks, on my shelves. There are some eight-inch disks stored in a box, somewhere, for historical purposes. I have several nine-track tapes that I use as show-and-tell items (I have a box of vacuum tubes for the same purpose). My data backups are on CDs and DVDs, and my desktop computer has an optical drive to read these. Most computers don't have an optical drive, since data storage is expected to be on USB flash drives, SD cards, or the "cloud."[1] I object to cloud computing, since I don't want to relinquish the safety of my data to another party. No matter what media are used, we always have the expectation that careful storage will allow our data to be read at any future time, provided we have a physical reader. |
| Eighty column punch-cards were once so common that artisans would make Christmas wreaths and Easter flowers from them. (Via Wikimedia Commons.) |
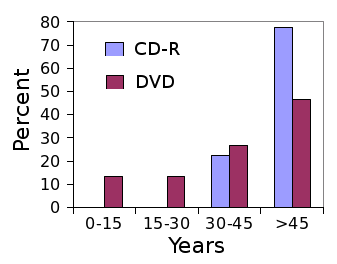 | Optical media lifetime, as determined by NIST. CD-R is more archival than DVDs (all types). (Graph rendered by author from data in ref. 1 using Gnumeric.)[1] |
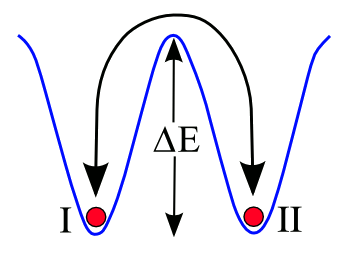 | Material stability modeled as an energy barrier ΔE between two states, I and II. (Illustration by by author using Gnumeric.)[1] |
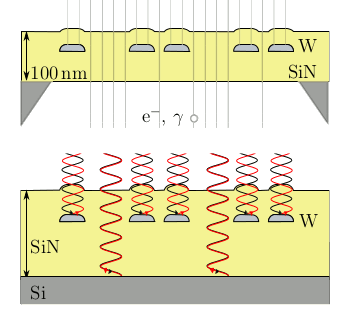
P = 1 - exp (-t/τ(T)In these equations, τ is the decay time, kB is the Boltzmann constant, T is the absolute temperature, and f0 is the attempt frequency. The attempt frequency can be estimated as the atomic vibration frequency, which can be as large as 1013 Hz. These equations allow a calculation of what the energy barrier must be for a desired media lifetime. Allowing for error correction, a million year memory needs an energy barrier of 63 kBT. Boosting the barrier just a little, to 70 kBT (1.8 eV at room temperature), gives you a billion year memory.[5] Scientists from the University of Twente (The Netherlands), the University of Freiburg (Germany) and KIST-Europe (Saarbrücken, Germany) have published a proposal for a billion year memory on arXiv.[5-6] It consists of a physical pattern of one material embedded in another, and they demonstrated such a memory with tungsten embedded in silicon nitride (Si3N4) (see figure). While using the Arrhenius law model, The authors caution against "black swan" events, such as "theft, meteor impact or the sun entering the red giant phase."[5] nanometer tungsten lines embedded in silicon nitride. Tungsten was chosen because of its high melting point (3422 °C) and low thermal expansion (4.5 x 10-6/K). Silicon nitride was chosen not only for its low thermal expansion (3.3 x 10-6/K), but its high fracture toughness and transparency to light; and, in a thin slab, its transparency to electrons. These two materials are commonly used in microfabrication, so fabrication processes are well developed.[5-6] According to the Arrhenius law model, a million year memory of this type, stored at room temperature, would need to survive for an hour at 445 kelvin (172 ° C). The memory survived this temperature, but there was significant information loss at 848 kelvin (575 ° C). The high temperature test was not really an appropriate aging test, since the thermal expansion difference between tungsten and silicon nitride caused cracks to appear.[5-6]
where
τ(T) = (1/f0) exp (ΔE/(kBT)
References:
- Technical people don't usually read poetry, but how can one not admire this verse from Shelley's poem, The Cloud:
That orb'ed maiden with white fire laden,
Percy Bysshe Shelley, "The Cloud," from English Poetry II: From Collins to Fitzgerald, (The Harvard Classics, 1909–14, via Bartleby.com).
Whom mortals call the moon,
Glides glimmering o'er my fleece-like floor,
By the midnight breezes strewn;- NIST/Library of Congress, Optical Disc Longevity Study, September 2007 (PDF File).
- John W. C. Van Bogart (National Media Lab), "Mag Tape Life Expectancy 10-30 years," Letter to the editor of the Scientific American, March 13, 1995.
- S. H. Charap, P. L. Lu, and Y. He, "Thermal stability of recorded information at high densities," IEEE Trans. Magn., vol. 33, no. 1 (January, 1997), pp.978-983.
- Jeroen de Vries, Dimitri Schellenberg, Leon Abelmann, Andreas Manz and Miko Elwenspoek, "Towards Gigayear Storage Using a Silicon-Nitride/Tungsten Based Medium," arXiv Preprint Server, October 9, 2013.
- Million-Year Data Storage Disk Unveiled, Technology Review, October 21, 2013.
- NIST/Library of Congress, Optical Disc Longevity Study, September 2007 (PDF File).