
Charles A. Walton and RFID
January 2, 2012Ken Olsen (February 20, 1926 - February 6, 2011)I didn't write about Steve Jobs, since articles about him have become a publishing industry in themselves, and my contribution would have been diluted many times over by more authoritative sources. I will admit that I bought my children a Franklin computer at one of their going-out-of-the-apple-clone-computer-business sales at a Trenton Computer Festival. I wasn't going to pay Apple prices for an Apple II computer. At one time there were many articles written about the "hidden" computers in your house. Nowadays, people expect everything from toasters to telephones to be computerized, so those articles aren't written anymore. Possibly the largest number of computer chips in a house are represented by one type of device, the radio frequency identification tag, commonly called an RFID. The inventor of RFID, Charles A. Walton, died on November 6, 2011, at age 89.[1-4] Walton was born on December 11, 1921, in Spondon, England, and he spent his youth in Maryland and New York.[4] He was awarded a BS degree in electrical engineering from Cornell University in 1943, and MS degrees in electrical engineering and economics of engineering from the Stevens Institute of Technology in 1950.[5] Walton served in the US Army Signal Corps during World War II, and he became a citizen of the United States in 1944.[4] Walton was an amateur radio operator, an avocation that likely helped in his development of RFID technology.[3] Walton joined IBM's research and development laboratories in 1960, where he worked for a decade on control systems and disc drives.[5] IBM eventually transferred him to Los Gatos, California, and he left IBM in 1970 to start Proximity Devices, a company that was based on his ideas for radio frequency identification devices. Walton patented many radio frequency identification circuits, and one of these patents was the first to use the acronym, RFID. [4] The idea of an RFID tag, a device that transmits identification information wirelessly to interrogation circuitry while simultaneously obtaining power from its radio frequency field, did not originate with Walton. The first such tags were made in 1969 by Mario W. Cardullo and Bill Parks of the Communications Satellite Corporation.[5-6] The Cardullo and Parks device was powered by the interrogation signal, and this technique is used by all inexpensive RFID tags, including the one disclosed in one of Walton's later patents, as shown in the figure.[7]
Harry Coover (March 6, 1917 - March 26, 2011)
William Lipscomb (December 9, 1919 - April 14, 2011)
Willard Boyle (August 19, 1924 - May 7, 2011)
Maurice Goldhaber (April 18, 1911 - May 11, 2011)
Hubert Schlafly (August 14, 1919 - April 20, 2011)
Robert A. Helliwell (September 2, 1920 - May 3, 2011)
Bob Pease (August 22, 1940 - June 18, 2011)
Thomas Peter Brody (April 18, 1920 – September 18, 2011)
Wilson Greatbatch (September 6, 1919 - September 27, 2011)
Lee Davenport (December 31, 1915 - September 30, 2011)
Dennis Ritchie (September 9, 1941 - October 12, 2011)
Herbert A. Hauptman (February 14, 1917 - October 23, 2011)
John McCarthy (September 4, 1927 - October 24, 2011)
Lynn Margulis (March 5, 1938 - November 22, 2011)
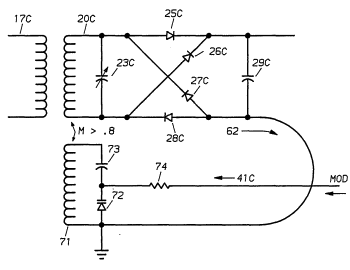 | Figure 4 of US Patent No. 4,580,041, "Electronic proximity identification system with simplified low power identifier," by Charles A. Walton, April 1, 1986. This circuit derives power from the RF field and provides a phase-modulated response signal. (Google Patents).[7] |
"It is an objective of the present invention to provide an electronic identification and recognition system adapted to identify an object having an electrical passive circuit and to indicate the identification of said object by digital electrical signals.Walton's royalty income from his patents ceased in the mid-1990s.[3] Today, many large organizations, such as Walmart and the US Department of Defense, have adopted RFID,[5] and the worldwide RFID market was forecast to have been about $6 billion in 2011.[3]
It is an objective of the present invention to provide a system which does not require mechanical engagement of the object to be identified with the detector and does not require optical or television systems.
It is an objective of the present invention to provide a system which is economical and capable of identifying objects rapidly.
It is a further objective of the present invention to provide a system adapted to identify or to recognize matching of a remote coded object with a sensor designed to react positively to said objects having a pre-specified code and negatively to objects having other than said pre-specified code."
 | An inexpensive RFID tag. The loop antenna, with its crossover and tuned capacitance sections, take the majority of the surface area. (Via Wikimedia Commons). |
References:
- Robert McMillan, "11 Who Died in 2011 (And Were Not Named Steve)," Wired, December 29, 2011.
- Charles Walton (inventor) on Wikipedia
- Dean Takahashi, "Charlie Walton, inventor of RFID, passes away at 89," Venture Beat, November 27, 2011.
- Charles Alfred Dodgson Walton, Obituary on Legacy.com.
- H. Mitchell, "Charles Walton," Inventor of the Week, Lemelson-MIT Program Web Site.
- Mario W. Cardullo and William L. Parks, "Transponder Apparatus And System," US Patent No. 3,713,148, January 23, 1973
- Charles A. Walton, "Electronic proximity identification system with simplified low power identifier," US Patent No. 4,580,041, April 1, 1986.
- Charles A. Walton, "Electronic Identification And Recognition System," US Patent No. 3,816,709, June 11, 1974.
- Charles Walton (inventor) on Wikipedia
